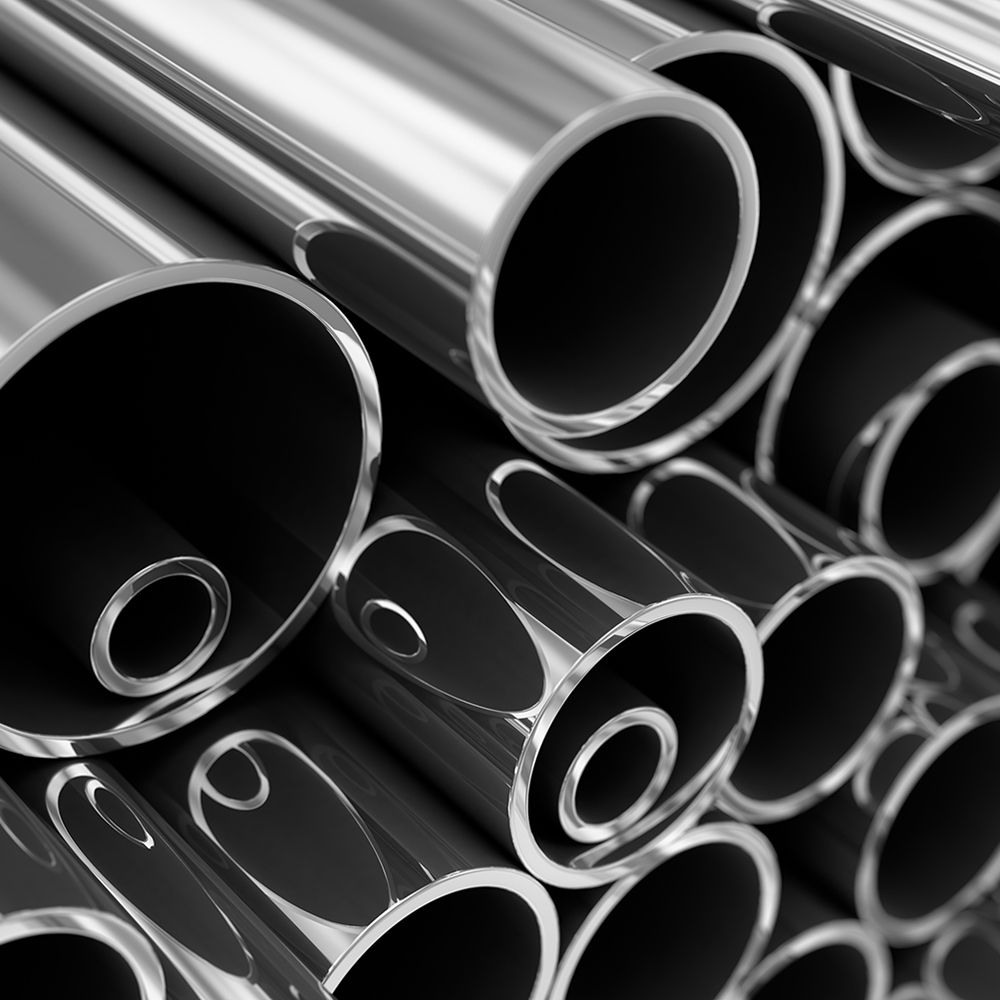
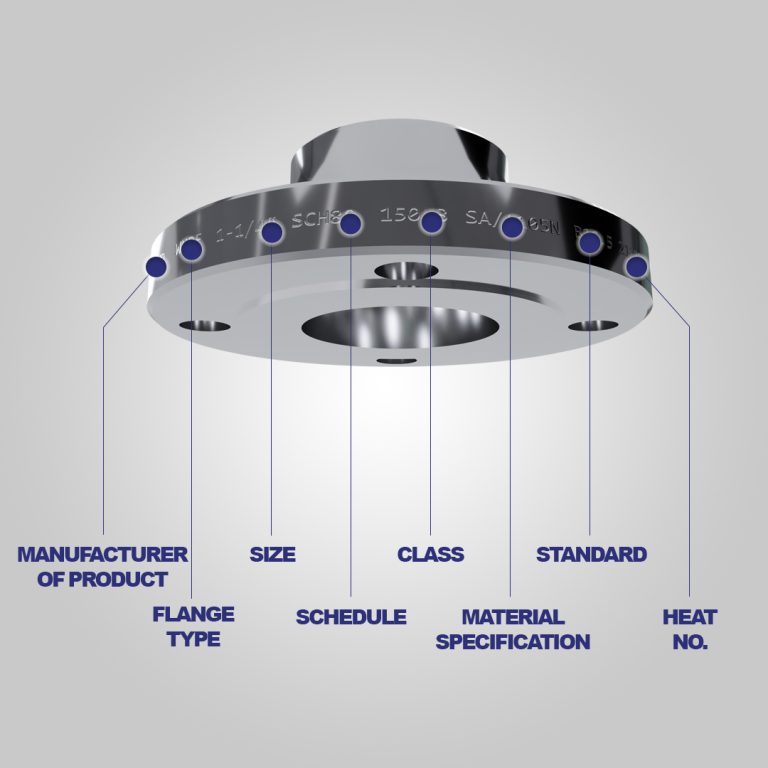
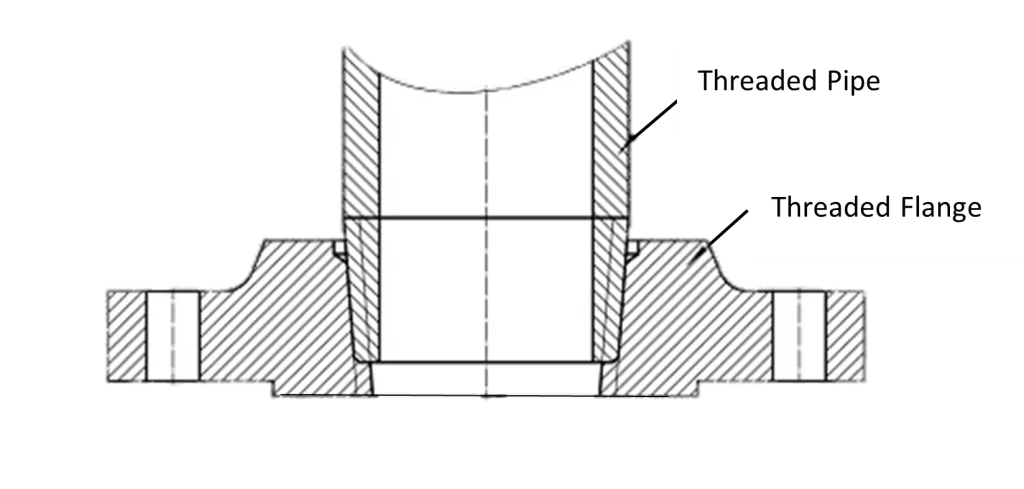
All You Need to Know About Stainless Steel Pipes
Stainless steel, a low-carbon steel with a minimum of 10% chromium, boasts corrosion-resistant properties due to the formation of a protective chromium oxide coating. This coating can self-heal in the presence of oxygen, enhancing longevity. Additional elements such as molybdenum, nickel, and nitrogen, along with increased chromium content, further improve corrosion resistance. With over 60 grades available, stainless steel is categorized into four classes based on alloying substances. At Saliran, we prioritize high-quality materials with superior corrosion resistance for various applications in Malaysia and beyond.
What is Stainless Steel?
In essence, stainless steel is a low-carbon steel that has at least 10% by weight of chromium. Chromium is added to steel to give it its special stainless, corrosion-resistance qualities. Because steel contains chromium, a tenacious, adherent, invisible, corrosion-resistant chromium oxide coating can develop on the steel surface.
This coat can self-heal if it sustains mechanical or chemical damage as long as oxygen is available, even in trace amounts. By adding other elements like molybdenum, nickel, and nitrogen as well as increasing the amount of chromium in the steel, the corrosion resistance and other beneficial qualities are improved. Stainless steel comes in more than 60 different grades. The entire group may be split up into four classes, though. Each is recognized by the alloying substances that have an impact on their microstructure and are given names.
At Saliran, we choose high-quality materials that exhibit high levels of corrosion resistance together with appropriate mechanical and physical qualities. Numerous applications and industrial sectors in and outside of Malaysia use our stainless steel pipes.
Exploring the Benefits and Characteristics of Stainless Steel Pipes
Due to the features they possess, stainless steel pipes are the most sought-after and searched-for pipes globally. When operating in any setting, such as chemical industries, cooking areas, hotter temperatures, and water supply regions, these High-temperature resistance pipes are the best and most dependable option. It provides the greatest quality, and the qualities it possesses make it exceptional and the ideal choice for many different fields.
Due to the wide range of components they include, which only adds to their versatility, they are pricey. It withstands trying circumstances and produces the greatest outcomes.
Properties of stainless pipe fittings in a nutshell:
- They don’t corrode
- They have a high strength rate
- These are robust
- They are ecologically beneficial since they are 100% recyclable
- They can be controlled and handled with ease
- These are long-lasting.
Match Your Needs with the Right Stainless Steel Pipe:
With more than ten years of experience in the trading and supply of premium Corrosion resistance steel pipes, Saliran Group has a large number of satisfied clients all over the world.
To satisfy your needs, we offer a range of Welded pipes with various standards and specifications.
However, when you are looking to buy stainless pipe fittings, consider the following things:
Quality:
Since quality cannot be compromised at any cost, it is always crucial to examine it. People frequently settle for substandard quality in their pursuit of lower prices, which leads to disastrous circumstances.
Therefore, it is usually preferable to use only high-quality stainless pipes to prevent accidents and other issues. High-quality SS pipes will be more durable and produce superior results.
Standardization and Certification:
When compared to products without one, those with certification and standardization represent the highest levels of performance and quality. Standardized items pass several tests to obtain certifications and provide you a guarantee, so you can always go and have your concerns heard, as opposed to uncertified products, which have no guarantee and won’t last for you over the long haul.
Here, it is important to note that Saliran is certified to the latest version of the industry standard ISO 9001:2015. To prepare individuals for a successful career with Saliran—at the vanguard of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (IR4.0)—the company offers extensive training programs. Employees use a hybrid approach to gain technical competence and certifications throughout the program.
Look for trustworthy sources and client testimonials:
We should constantly think about the people we know before making any kind of purchase since we can trust them to give us the proper service and point us in the right route. It’s because you have a strong relationship with them, a solid connection, and reliability that works in your favor.
For instance, if an issue with the product arises in the future, they will always consider it and offer the finest services, sometimes for a longer period. After that, you may search for further choices, but only those that are also dependable. To determine a product’s dependability, it’s crucial to read prior customer evaluations from credible sources because they will point you on the proper path.
You can operate more effectively, consistently, and securely because of Saliran’s committed workforce, cutting-edge technology, and worldwide reach and capabilities. Building a world that flows smoothly is the irrepressible purpose of Saliran Industrial Supplies and Saliran Precision Engineering, which is supported by cutting-edge technology, a vast worldwide network, and an outstanding workforce.
Visit our website if you want to buy anything but can’t locate the correct supplier. Saliran Group is a global marketplace that links reputable suppliers and clients with engineering tools and services. On our website, we have provided you with a list of trustworthy connections for vendors and exporters. You may browse that list and select the best alternative from the many possibilities there.
Product Tags
Welded Line Pipe | |
Thickness | 1/8" (6mm), 1/4" (8mm), 3/8" (10mm), 1/2" (15mm), 3/4" (20mm), 1" (25mm), 1-1/4" (32mm), 1-1/2" (40mm), 2" (50mm), 2-1/2" (65mm), 3" (80mm), 3-1/2" (90mm), 4" (100mm), 5" (125mm), 6" (150mm), 8" (200mm) |
Standard | API 5L, ASME/ANSI B36.10 |
NDT | API 5L Annex E (as per client requirement) |
Heat Treatment | As per request |
Coating | Internal and external coating available as per request |
Specification | |
Carbon Steel | API 5L Gr.B |
High Yield Carbon Steel | API 5L X42/ 46/ 52/ 60/ 65/ 70 - PSL1/2 |
Low Temp Carbon Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A671 CC65 CL22 |
Stainless Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A312 304/304L, 316/316L, 317/317L,321/321H,310 |
Duplex / Super Duplex | UNS S31803, S32205, S32750, S32760, S31254 |
Size Range | |
ERW | 2" (50mm), 2-1/2" (65mm), 3" (80mm), 3-1/2" (90mm), 4" (100mm), 5" (125mm), 6" (150mm), 8" (200mm), 10" (250mm), 12" (300mm), 14" (350mm), 16" (400mm), 18" (450mm) |
LSAW | 16" (400mm), 18" (450mm), 20" (500mm), 22" (550mm), 24" (600mm), 26" (650mm), 28 (700mm)", 30" (750mm), 32" (800mm), 34" (850mm), 36" (900mm), 38" (950mm), 40" (1000mm), 42" (1050mm), 44" (1100mm), 46" (1150mm), 48" (1200mm), 50" (1250mm), 52" (1300mm), 54" (1350mm), 56" (1400mm), 58" (1450mm), 60" (1500mm) |
Seamless Pipe | |
Size Range | 1/4" (8mm), 3/8" (10mm), 1/2" (15mm), 3/4" (20mm), 1" (25mm), 1-1/4" (32mm), 1-1/2" (40mm), 2" (50mm), 2-1/2" (65mm), 3" (80mm), 3-1/2" (90mm), 4" (100mm), 5" (125mm), 6" (150mm), 8" (200mm), 10" (250mm), 12" (300mm), 14" (350mm), 16" (400mm), 18" (450mm), 20" (500mm), 22" (550mm), 24" (600mm), 26" (650mm), 28 (700mm)", 30" (750mm), 32" (800mm), 34" (850mm), 36" (900mm), 38" (950mm), 40" (1000mm), 42" (1050mm), 44" (1100mm), 46" (1150mm), 48" (1200mm) |
Schedule | SCH 10, SCH 20, SCH 30, SCH 40, SCH 60, SCH 80, SCH 100, SCH 120, SCH 140, SCH 160 SCH STD, SCH XS, SCH XXS, SCH 10s, SCH 40s, SCH 80s |
Standard | ASME/ANSI B36.10, B36.19 |
Specification | |
Carbon Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A106 Gr A/ Gr B/ Gr C |
High Yield Carbon Steel | API 5L X42/ 46/ 52/ 60/ 65/ 70 - PSL1/ 2 |
Low Temp Carbon Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A333 Grade 6 |
Chrome Moly | ASME/ASTM SA/A 335 Grade P5/ P11/ P22/ P91 |
Stainless Steel | ASME/ ASTM SA/A312 TP304/304L, 316/316L, 309, 309H, 310S, 310H, 317/317L, 321, 321H, 347, 347H, 904L |
Duplex/ Super Duplex | ASME/ASTM SA/A790 UNS S31803, S32205, S32750, S32760 |
Nickel Alloy | ASME/ASTM SB163, 168, 424, 443, 575 UNS N02200 (Nickel 200), UNS N02201 (Nickle 201) UNS N04400 (Monel 400), UNS N06600 (Inconel 600) UNS N06601 (Inconel 601), UNS N06625 (Inconel 625) UNS N08810 (Incoloy 800H), UNS N08811 (Incoloy 800HT) |
Remark | HIC, PED 2014/68/EU, NACE MR0175, NORSOK available |
Looking for flanges, fittings, pipes, valves and gasket?
Saliran Group has over 10 years of experiences in trading of a wide range of flanges, pipes, valves, fittings, gasket and related parts and accessories (“PVF products”) as well as steel products with numerous happy customers all around the world. We supply a variety of gaskets either in metal, non-metal as well as food-grade approval available material.
Click on the link below to contact us now!