
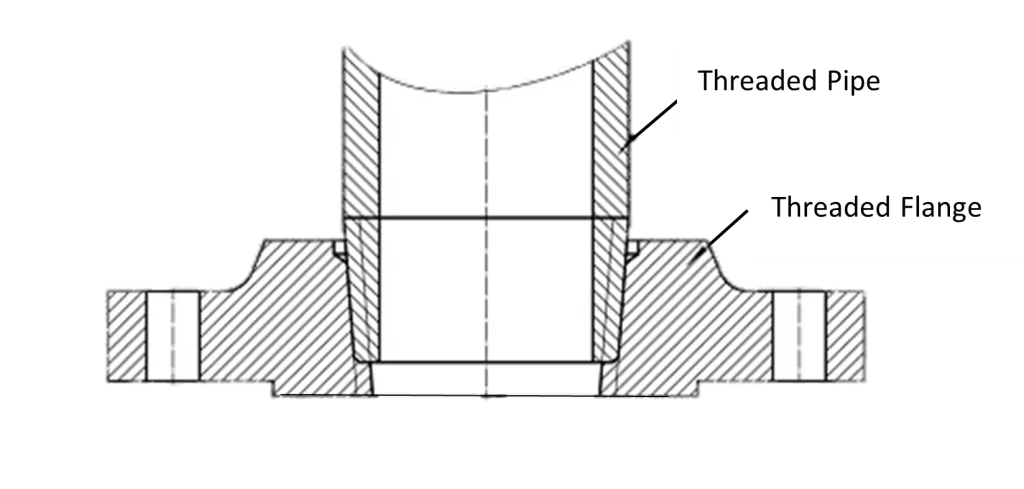
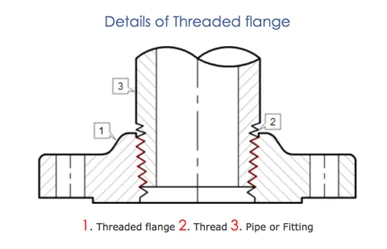
Threaded flange, also known as screwed flange, has a thread inside the flange bore that fits on the pipe with a matching male thread. This type of joint connection is quick and easy to use. However, threaded flange is not suitable for high pressure or temperature applications. Threaded flange is commonly used in utilities such as air and water.
What is a Threaded Flange?
Threaded flange is similar to slip on flange except that the bore is threaded. It can be assembled without welding. This explains its use in low pressure services at normal atmospheric temperatures and in highly explosive areas where welding poses a risk. As the tapers approach the same diameter, the threads seal between the threaded flange and the pipe. In addition to the threaded connection, a seal weld is sometimes used.
Also, they are available in a variety of sized and materials. The thread must be concentric with the axis of the flange opening, and alignment variations (perpendicular to the flange face) must be not more than 5mm per metre. Threaded flanges are available in NPS 1/2 through NPS 24 sizes and pressure ratings of Class 150, 300, 400, 600, and 900. NPS 1/2 to NPS 2-1/2 are available in Class 1500 and Class 2500 sizes.
Key Characteristics of Threaded Flange
- No welding is required.
- Extremely good for small pipe sizes.
- Larger load, especially when subjected to higher torque, should be avoided.
Uses of Threaded Flange
- Threaded flanges can be fitted to pipes of various sizes without welding. It is one of the main reasons why these flanges are so popular.
- It can be used in extremely high-pressure applications, particularly where post-weld heat treatment is not possible.
- It is ideal for piping with small diameters.
- Cost-effective and time-saving diameters.
- Threaded flanges are typically used in non-cyclic applications.
- The flanges can be used in applications where welding is dangerous.
- It can be used in potentially explosive environments.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Threaded Flange
- Advantages
- The threaded flange joint does not require welding to be assembled. Also, a pipe with tapered threads on both ends can be easily assembled with the threaded flange. Because of this feature, the threaded flange is well-suited to extreme pressure services that operate at normal ambient temperatures. And also, in highly explosive areas where welding may pose a hazard.
- Disadvantages
- The disadvantages of threaded flanges are obvious as well. The crevices formed between the external and internal threads have the potential to easily capture and retain process fluid. This makes the threaded connection vulnerable to crevice corrosion. It occurs when process fluid penetrates the thread region and causes failure. Furthermore, threaded joints are also significant stress risers. A relatively small number of cycles of expansion and contraction or movement brought on by misalignment may cause the threaded flange to fail. This is because of tightening increases stress in the thread region.
- Besides that, threaded steel flanges are typically limited to water or air services in sizes NPS 6 (DN 150) or smaller, with a design temperature of no more than 250 °F. They are also not suitable for high temperature, cyclic stress, or corrosive fluid conditions. The dimensional tolerances of threaded flanges are nearly identical to those of slip on flanges.
Product Tags
Type | Blind Flange, Slip on Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Socket Weld Flange, Threaded Flange, Lap Joint Flange, Anchor Flange, Orifice Flange |
Size Range | 1/2" (15mm) - 48" (1200mm) |
Class | 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, 2500# |
Type Available | Raised Face RF, Ring Type Joint RTJ, Flat Face FF, Male & Female M&F, Tongue Groove T&G |
Schedule | SCH 10, SCH 20, SCH 30, SCH 40, SCH 60, SCH 80, SCH 100, SCH 120, SCH 140, SCH 160 SCH STD, SCH XS, SCH XXS SCH 10s, SCH 40s, SCH 80s |
Standard | ASME B16.1, ASME B16.5, ASME B16.20, ASME B16.21, ASME B16.24, ASME B16.34, ASME B16.36, ASME B16.42, ASME B16.47 MSS SP-6, MSS SP-9, MSS SP-25, MSS SP-44, MSS SP-53, MSS SP-54, MSS SP-55, MSS SP-75, MSS SP-106 API 605, API 6A, API 6B |
Specification | |
Carbon Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A105N |
High Yield Carbon Steel | ASTM A694 F42/ 46/ 52/ 60/ 65/ 70 ASTM A707 L1~ L8 |
Low Temp Carbon Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A350 LF1/ 2/ 3/ 6 |
Chrome Moly | ASME/ASTM SA/A182F2, F5 ,F9, F11, F12, F22, F91 |
Stainless Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A182F304/304L, 316/316L, 309, 310, 304H, 310H, 317/317L, 321, 321H, 347, 347H, 904L |
Duplex/ Super Duplex | UNS S31803, S32205, S32750, S32760 |
Nickel Alloy | ASME/ASTM SB564, |
Remark | HIC, PED 2014/68/EU, NACE MR0175, NORSOK, Weld Overlay available |
flanges supplier malaysia
Looking for flanges, fittings, pipes, valves and gasket?
Saliran Group has over 10 years of experiences in trading of a wide range of flanges, pipes, valves, fittings, gasket and related parts and accessories (“PVF products”) as well as steel products with numerous happy customers all around the world. We supply a variety of gaskets either in metal, non-metal as well as food-grade approval available material.
Click on the link below to contact us now!



