The flange is a ring-shaped device that can be used instead of welding or threading various piping system components used throughout the piping system. Because they may be easily dismantled for transportation, routine inspection, maintenance, or replacement, flanged connections are used as an alternative to welding. Because threading large bore pipe is neither cheap nor dependable, flange ends are preferred. The flange is an essential part of every plumbing system. Flanges are most commonly employed when connecting or disassembling a junction is required. Flanges can be found in pipe-to-fitting joints, valves, equipment, or any other important component of the piping system.
Flange Parts
A typical flanged connection is comprised of three parts:
- Pipe
- Flanges
- Gasket
- Bolting
Common Flange Types and Characteristics
Flanges are not a one-size-fits-all answer. Aside from sizing, selecting the best flange design for your piping system and intended use will help to assure dependable performance, a long service life, and a competitive price.
Here are some of the most prevalent flange types:
Threaded Flange
Socket-Weld Flange
Slip-On Flange
Lap Joint Flange
Lap joint flanges are two-piece designs that require butt welding the stub end to the pipe or fitting and the use of a backing flange to produce the flanged connection. Because of this, this type is ideal for usage in systems with limited physical area or systems that require frequent disassembly and repair.
Weld Neck Flange
Blind Flange
Specialty Flange
Nipple flanges, an essential component of fluid conveyance systems, securely join pipes and fittings. These threaded extensions are short and offer leak-free couplings and ease of installation. Nipple flanges, known for their adaptability, play an important part in a variety of sectors, from plumbing to oil and gas, guaranteeing efficient fluid movement.
Orifice flanges are critical components of fluid measuring and control systems. They have a precision-drilled hole that allows for accurate flow rate and pressure monitoring. These flanges are widely used in industries such as petrochemicals and manufacturing, where they ensure accurate fluid management and efficient processes.
Long weld neck flanges are designed for important applications requiring strength and integrity. Their expanded neck design provides additional support, decreasing joint stress. These flanges are extensively used in industries such as oil & gas and power generation and are ideal for high-pressure systems.
Flange Facing Types
-
- Flat Face (FF): As the name implies, flat face flanges have a flat, even surface with a full face gasket that contacts the majority of the flange surface.
- Raised Face (RF): These flanges have a little elevated area around the bore and an inside bore circle gasket.
- Ring Joint Face (RTJ): This face type is used in high-pressure and high-temperature procedures and has a groove in which a metal gasket sits to maintain the seal.
- T&G (Tongue-and-Groove): These flanges have matching grooves and elevated portions. The design facilitates installation by allowing the flanges to self-align and providing a reservoir for gasket glue.
- Male and female (M&F) flanges: These flanges, like tongue and groove flanges, use a matching pair of grooves and raised parts to hold the gasket. Unlike tongue and groove flanges, however, these keep the gasket on the female face, allowing for more accurate positioning and a wider range of gasket material alternatives.
Flange Dimensions
Apart from a flange’s functional design, flange dimensions are the most probable factor to influence flange selection when developing, maintaining, or updating a pipe system. To ensure adequate sizing, consider how the flange interfaces with the pipe and the gaskets in use.
Common factors to consider include:
- Outside diameter: The distance between two opposing flange face edges.
- Thickness: The thickness of the outer adhering rim.
- Bolt circular size: The distance calculated from center to center between opposing bolt holes
- Pipe size: A reference to the pipe size to which the flange relates.
- Nominal bore size: The inner diameter of the flange connector.
Flange Classification and Service Ratings
Flanges are frequently classified according to their capacity to tolerate high temperatures and pressures. This is denoted by a number followed by the “#,” “lb,” or “class” suffix. These suffixes are interchangeable, but they will vary depending on the location or provider.
Typical classifications include:
- 150#
- 300#
- 600#
- 900#
- 1500#
- 2500#
The exact pressure and temperature tolerances will vary depending on the materials utilized, the flange design, and the flange size. The sole constant is that pressure ratings decline as temperatures rise in all circumstances.
Product Tags
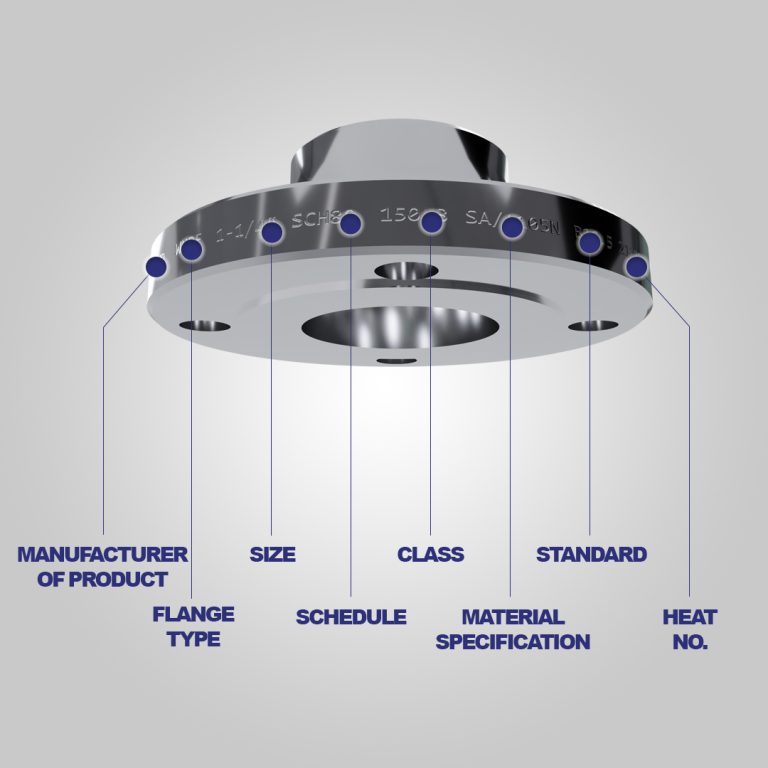
Flange Standards and Markings
Flanges are classified as global standards created by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) – ASME B16.5 & B16.47.
To aid in the replacement or verification of existing parts, all flanges must carry markings – often on their outer perimeter.
These markers are also in a certain order:
- Logo or code of the manufacturer
- ASTM material code
- Material Grade
- Service rating (Pressure-temperature Class)
- Dimensions
- Thickness (Schedule)
- Special designations, if applicable — for example, QT for quenched and tempered or W for welding repair
Type | Blind Flange, Slip on Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Socket Weld Flange, Threaded Flange, Lap Joint Flange, Anchor Flange, Orifice Flange |
Size Range | 1/2" (15mm) - 48" (1200mm) |
Class | 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, 2500# |
Type Available | Raised Face RF, Ring Type Joint RTJ, Flat Face FF, Male & Female M&F, Tongue Groove T&G |
Schedule | SCH 10, SCH 20, SCH 30, SCH 40, SCH 60, SCH 80, SCH 100, SCH 120, SCH 140, SCH 160 SCH STD, SCH XS, SCH XXS SCH 10s, SCH 40s, SCH 80s |
Standard | ASME B16.1, ASME B16.5, ASME B16.20, ASME B16.21, ASME B16.24, ASME B16.34, ASME B16.36, ASME B16.42, ASME B16.47 MSS SP-6, MSS SP-9, MSS SP-25, MSS SP-44, MSS SP-53, MSS SP-54, MSS SP-55, MSS SP-75, MSS SP-106 API 605, API 6A, API 6B |
Specification | |
Carbon Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A105N |
High Yield Carbon Steel | ASTM A694 F42/ 46/ 52/ 60/ 65/ 70 ASTM A707 L1~ L8 |
Low Temp Carbon Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A350 LF1/ 2/ 3/ 6 |
Chrome Moly | ASME/ASTM SA/A182F2, F5 ,F9, F11, F12, F22, F91 |
Stainless Steel | ASME/ASTM SA/A182F304/304L, 316/316L, 309, 310, 304H, 310H, 317/317L, 321, 321H, 347, 347H, 904L |
Duplex/ Super Duplex | UNS S31803, S32205, S32750, S32760 |
Nickel Alloy | ASME/ASTM SB564, |
Remark | HIC, PED 2014/68/EU, NACE MR0175, NORSOK, Weld Overlay available |
Looking for flanges, fittings, pipes, valves and gasket?
Saliran Group has over 10 years of experiences in trading of a wide range of flanges, pipes, valves, fittings, gasket and related parts and accessories (“PVF products”) as well as steel products with numerous happy customers all around the world. We supply a variety of gaskets either in metal, non-metal as well as food-grade approval available material.
Click on the link below to contact us now!